Azure for AWS professionals - Networking - Azure Virtual Networks vs AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
@20aman Sep 29, 2019Note that this post is a part of the series. You can view all posts in this series here: Azure for AWS professionals - Index
Microsoft Azure and Amazon's AWS cloud platforms provide networking as part of the Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Both provide similar services with some differences in the implementation of these services. Microsoft has named it's service as "Virtual Networks", whereas Amazon calls its service as "Virtual Private Cloud" or most commonly called as "VPC".
Both Microsoft Azure Virtual Networks and AWS VPC have "Subnets" inside a network. The VMs in Azure or EC2 instances in AWS has network interfaces that connects to the subnets within the Virtual Networks (or VPCs) and receive an IP address from that subnet. The traffic route inside these networks is governed by "Route Tables".
Traffic restrictions are implemented slightly differently in the two platforms. Microsoft Azure has "Network Security Groups". These can be applied at either Subnet or Virtual Machine level. Whereas AWS has Network Access Control Lists or ACLs that are applied at the subnet level. Also, AWS has Security Groups that are applied to the EC2 instances.
Accessing Microsoft Azure Virtual Networks
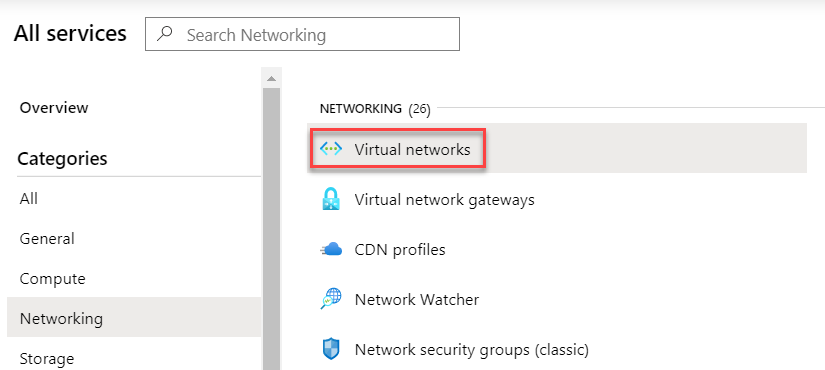
To view Virtual Networks in Azure, navigate to All services and then "Virtual Networks" under the Networking category.
Accessing AWS Virtual Private Clouds or VPCs
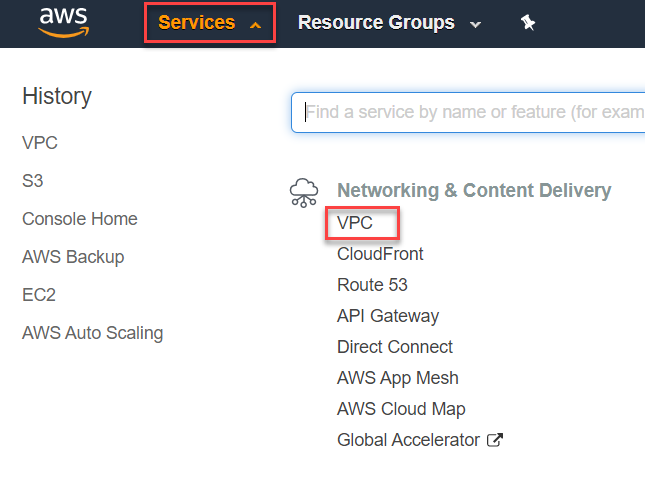
To view the VPCs, navigate to All Services and then click on VPC under the Networking category.
We will be looking at how to work with these services in detail in the next few posts.
For more information, click on the below official links: Azure Virtual Network Amazon Virtual Private Cloud